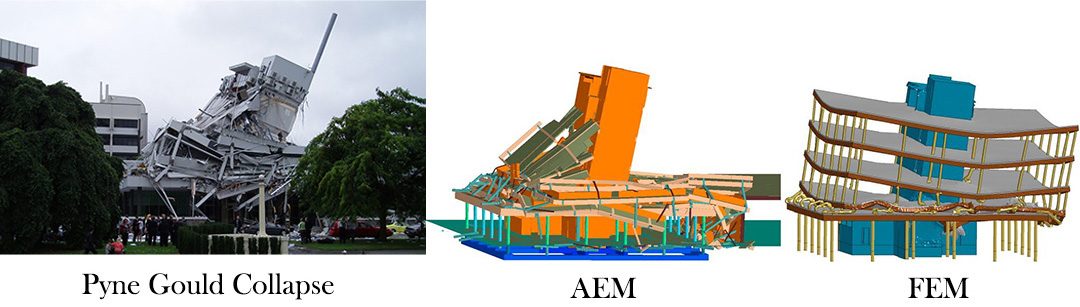
Reliability of collapse simulation – Comparing finite and applied element method at different levels
Numerical prediction of progressive collapse of buildings due to extreme loading is still a challenging task. However, increased computational power makes it nowadays possible to analyze not only small-scale connections and mid-size building elements, but also full buildings with considerable height and complexity. The present paper compares the results of Finite Element Method (FEM) and Applied Element Method (AEM) simulations to experimental results when performing blast or earthquake analysis on those three scales. The aim is to highlight which level of physical detail and complexity is required to predict progressive collapse numerically, and which level of accuracy can be expected. For the full scale level, the progressive collapse of the Pyne Gould Corporation Building in Christchurch, New Zealand, was simulated and compared to the final collapse shape. It is shown that the FEM is able to predict the structural response of small scale models well, but fails to achieve realistic collapsed shapes in case of the large structure, whereas the AEM shows convincing results in all cases.
Research and Practice on Progressive Collapse and Robustness of Building Structures in the 21st Century
Extreme events (i.e. terrorist attacks, vehicle impacts, explosions, etc.) often cause local damage to building structures and pose a serious threat when one or more vertical load-bearing components fail, leading to the progressive collapse of the entire structure or a large part of it. Since the beginning of the 21st century there has been growing interest in the risks associated with extreme events, especially after the attacks on the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma in 1995 and on the World Trade Center in New York in 2001. The accent is now on achieving resilient buildings that can remain operational after such an event, especially when they form part of critical infrastructures, are occupied by a large number of people, or are open to the public. This paper presents an ambitious review that describes all the main advances that have taken place since the beginning of the 21st century in the field of progressive collapse and robustness of buildings.
Using the Applied Element Method to simulate the dynamic response of full-scale URM houses tested to collapse or near-collapse conditions
In this work, the Applied Element Method (AEM) is employed to reproduce the dynamic response of three full-scale unreinforced masonry (URM) house specimens tested on a shake-table. Two of the test specimens correspond to a calcium-silicate terraced house typology...The Applied Element Method and the modelling of both in-plane and out-of-plane response of URM walls
TThe Applied Element Method (AEM) is a relatively recent addition to the discrete elements methods family. Initially conceived to model blast events and concrete structures, its use in the modelling of masonry structures subjected to earthquake actions is steadily...Using the applied element method for modelling calcium silicate brick masonry subjected to in‐plane cyclic loading
The response of calcium silicate unreinforced masonry construction to horizontal cyclic loading has recently become the focus of experimental and numerical research, given its extensive use in some areas of the world that are now exposed to induced earthquakes (eg,...Evaluation of the Seismic Retrofitting of an Unreinforced Masonry building using Numerical Modeling and Ambient Vibration Measurements
Ambient vibration measurements and 3-D nonlinear time-history numerical modeling are used to assess the retrofitting measures conducted in a 6-story unreinforced masonry building (URM) built in the end of the 19th century in Switzerland. Retrofitting measures were taken in order to improve the soundproofing and possibly the seismic performance of the building. Reinforced concrete (RC) footings were added under the walls and horizontal steel beams were added to link the walls together with a RC slab at each floor, though the wooden beams were left in place. Several ambient vibration recordings were performed before, during and after the retrofitting work in order to monitor the evolution of the dynamic behavior of the structure. Moreover, numerical models representing the state of the building before and after the retrofit work have been developed to perform nonlinear dynamic analyses using various ground motion records.
Simulation of the Dynamic Response of Steel Moment Frames following Sudden Column Loss. Experimental Calibration of the Numerical Model and Application
Significant research effort has been devoted in recent years to the evaluation of the capacity of steel frame structures to resist progressive collapse after sudden column loss. Due to the complex load-structure interaction and material behaviour, it can be very difficult to evaluate the ultimate capacity of structural components using current analytical methods. Therefore considerable research effort has been directed to experimental testing and sophisticated numerical simulations. Although sudden column loss is a dynamic process, most experimental studies on fullscale or scaled down specimens were performed under quasi-static loads. This paper presents the results of a study devoted to the evaluation of steel frame response following the loss of a column. Advanced numerical models are calibrated using experimental test results and dynamic increase factors are studied. Several full-scale structures are investigated for a sudden column loss scenario.
Seismic Vulnerability Assessment Of “Sion Cathedral” (Switzerland): An Integrated Approach To Detect And Evaluate Local Collapse Mechanisms In Heritage Buildings
Seismic assessment of existing heritage buildings remains a challenging task. There is a high level of complexity and uncertainty compared with the assessment of standard buildings. Heritage masonry churches are usually prone to partial collapses during earthquake due to local loss of stability, and exhibit particular seismic vulnerabilities. An important step in the seismic analysis of heritage masonry buildings is the detection of local mechanisms. The Italian Building Code provides a simplified approach (LV1-churches) to assess the vulnerability of heritage churches evaluating and comparing 28 potential mechanisms. A general index of vulnerability and hierarchy between mechanisms is thereby provided. Verification of safety against local mechanisms can also be carried out using the kinematic approach. This procedure is based on evaluating the horizontal action needed to activate out-of-plane collapse mechanisms. Based on a full-scale study (Sion Cathedral), this paper evaluates the reliability of the “LV1-church” approach and of the kinematic approach through a comparison with the results obtained with a complex 3D model using the Applied Element Method.
Usefulness of ambient-vibration measurements for seismic assessment of existing structures
A large number of buildings in regions with low to medium seismic hazard have been designed without considering earthquake actions. Retrofitting of all buildings that fail to meet modern code requirements is economically, technically and environmentally unsustainable. Decision-making regarding retrofitting necessity and prioritization is complex. Ambient vibrations are non-destructive and easy to measure, and thus an attractive data source. However, ambient vibrations have very low amplitudes, which potentially lead to sensitivity to testing conditions and stiffness contributions from non-structural elements. Seismic assessment necessitates non-linear behavior extrapolation from linear measurements, which results in biased model predictions.
